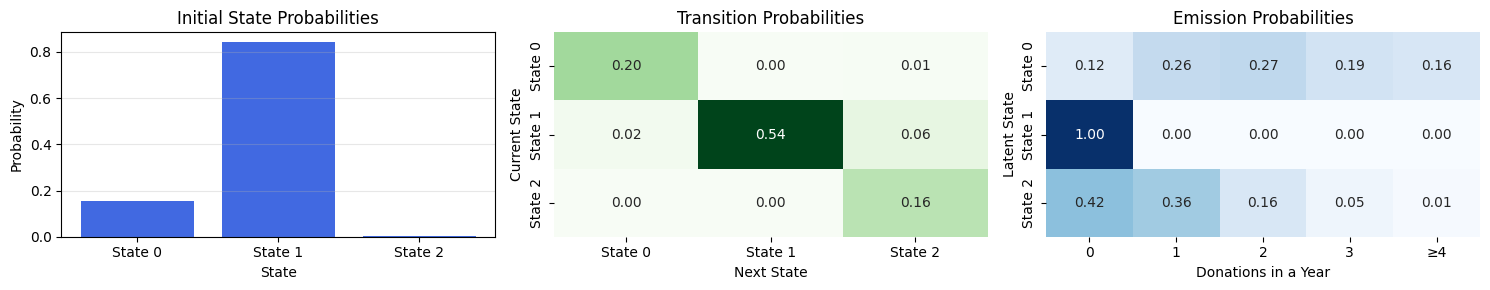
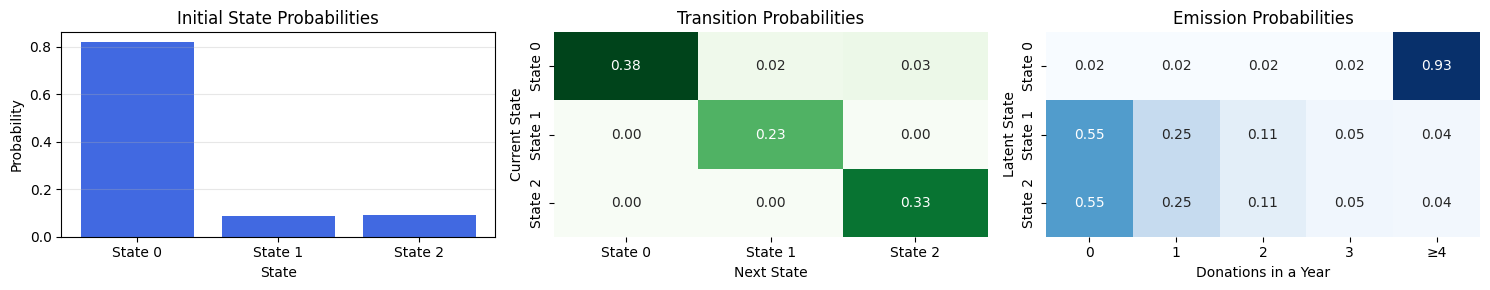
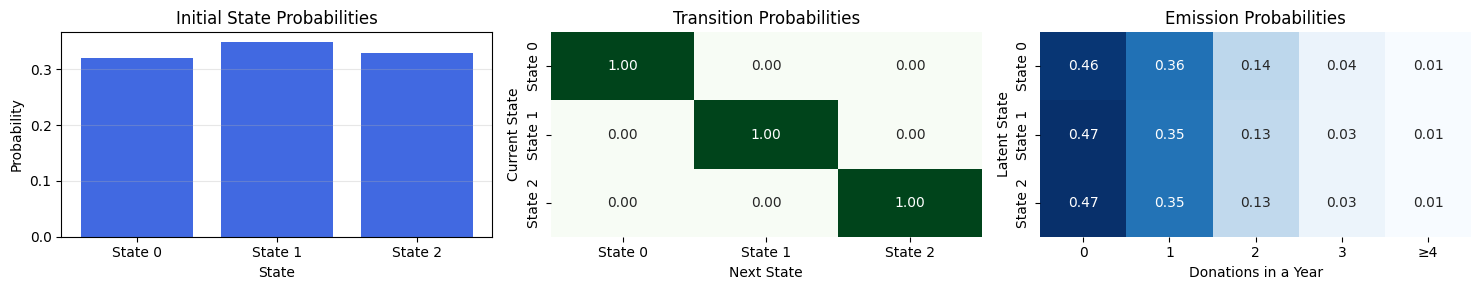
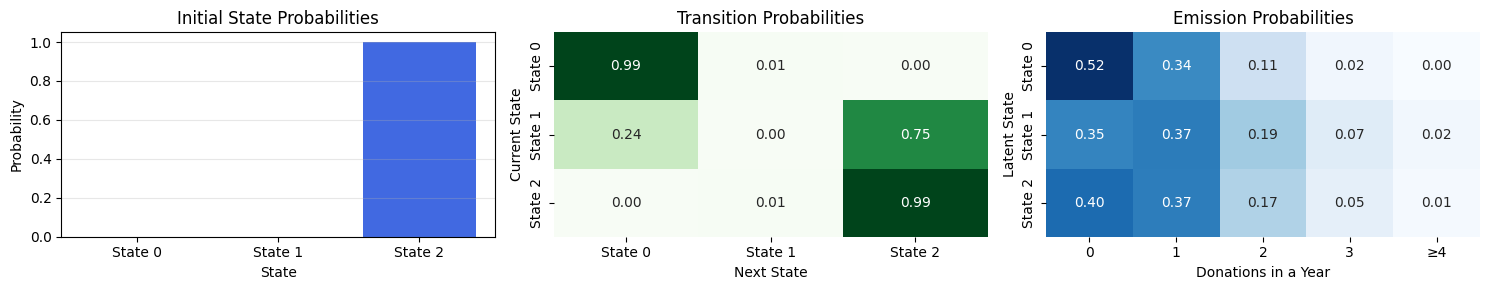
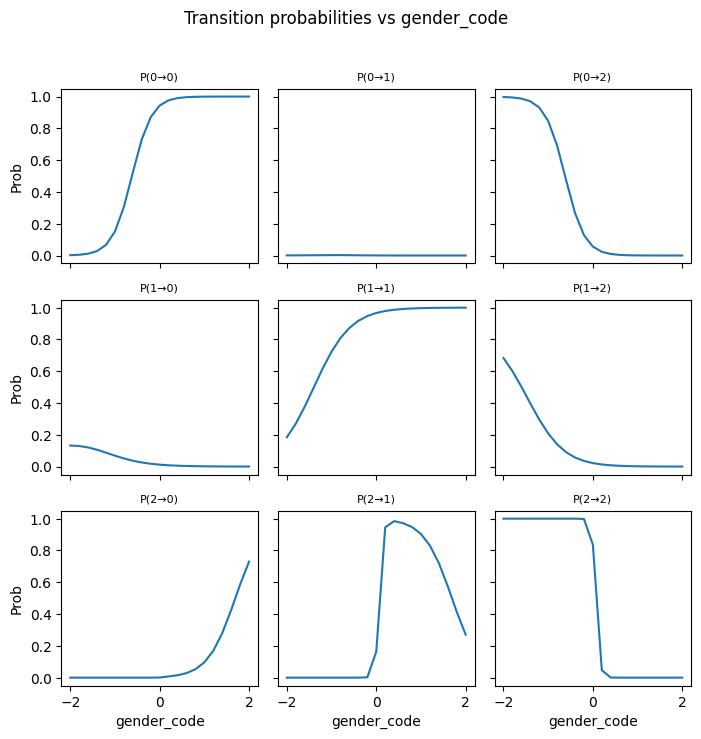
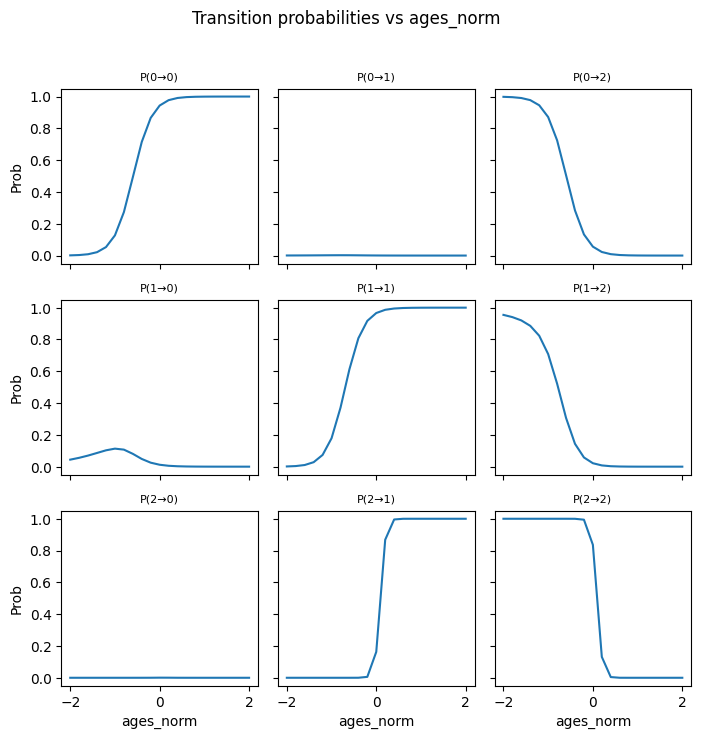
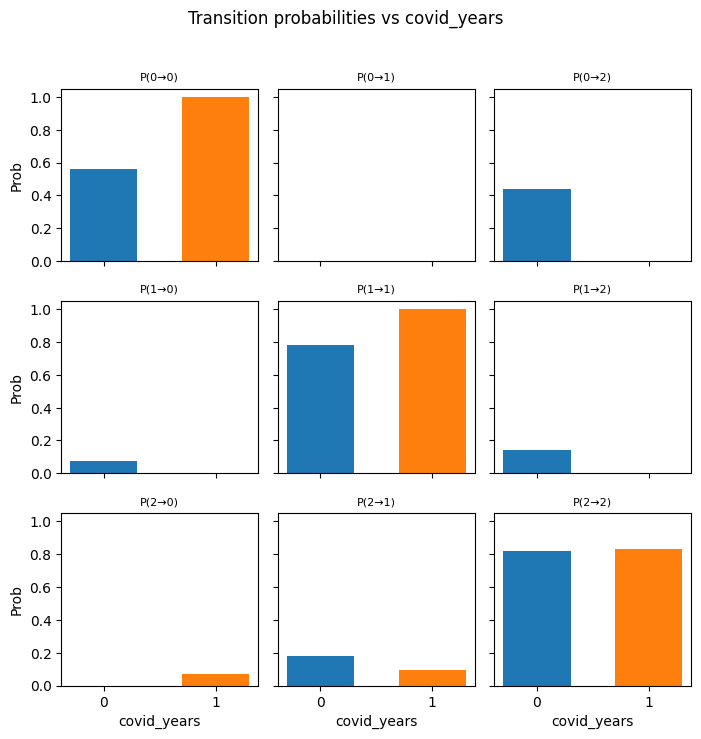
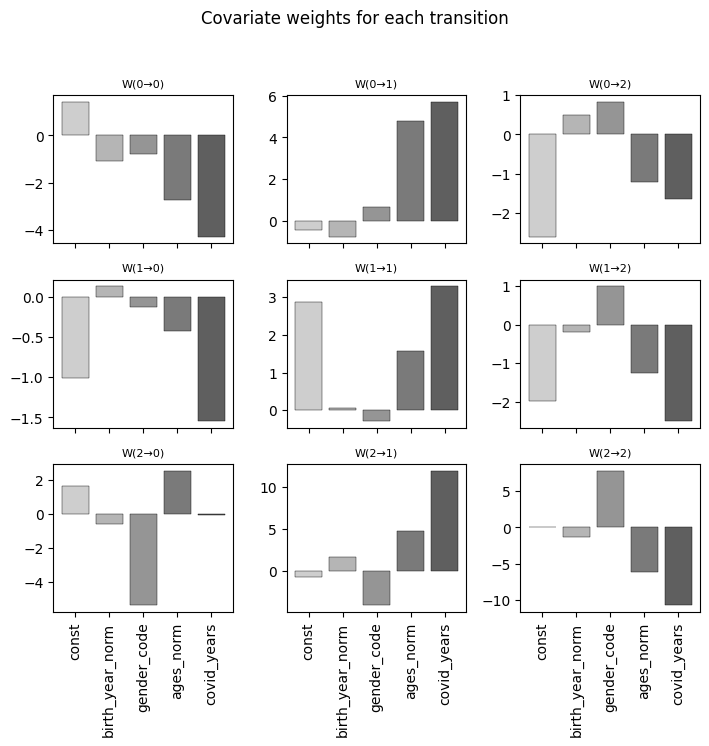
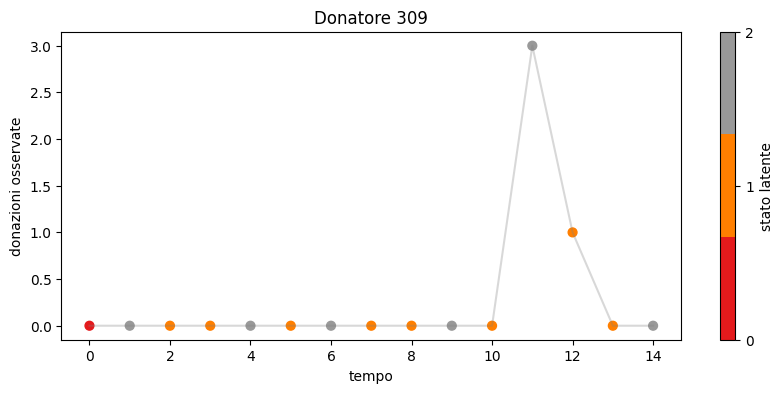
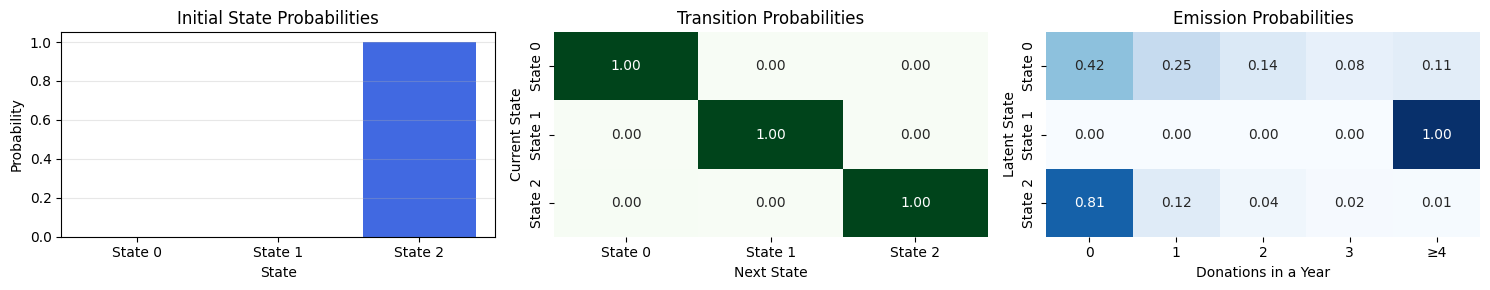
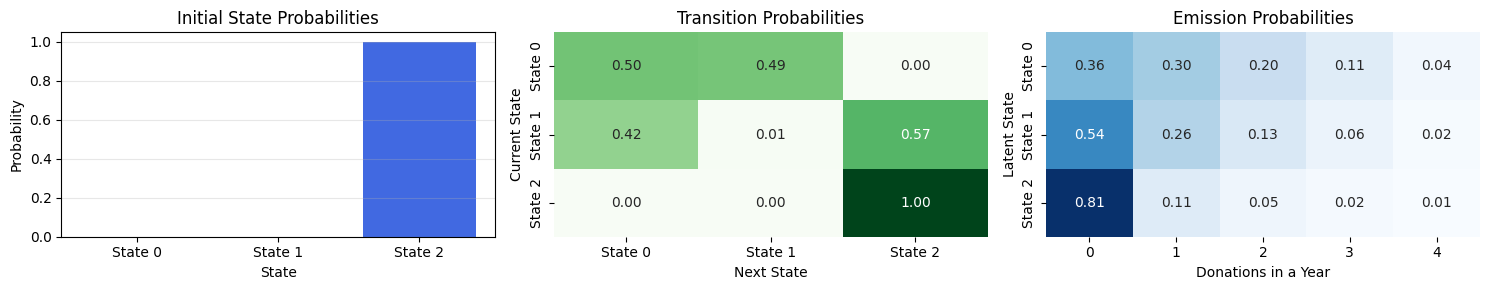
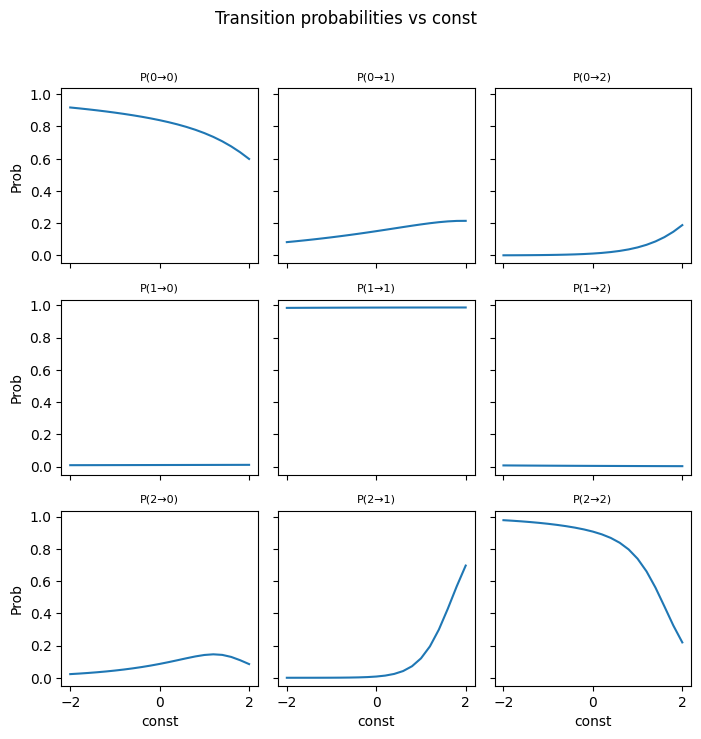
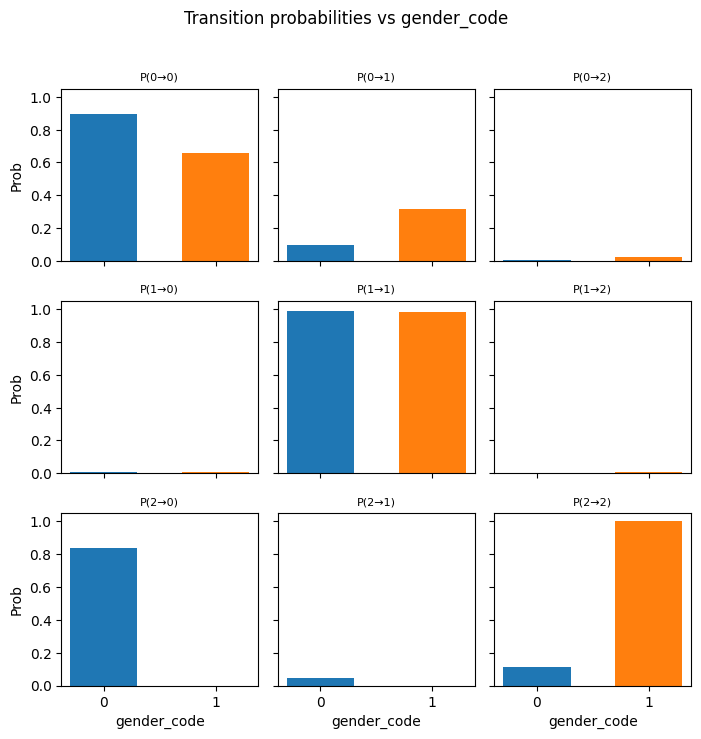
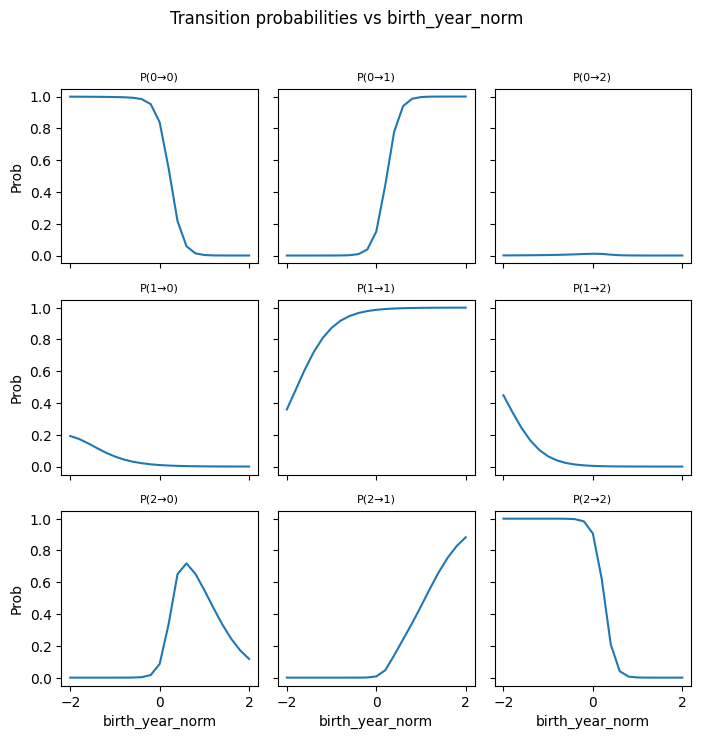
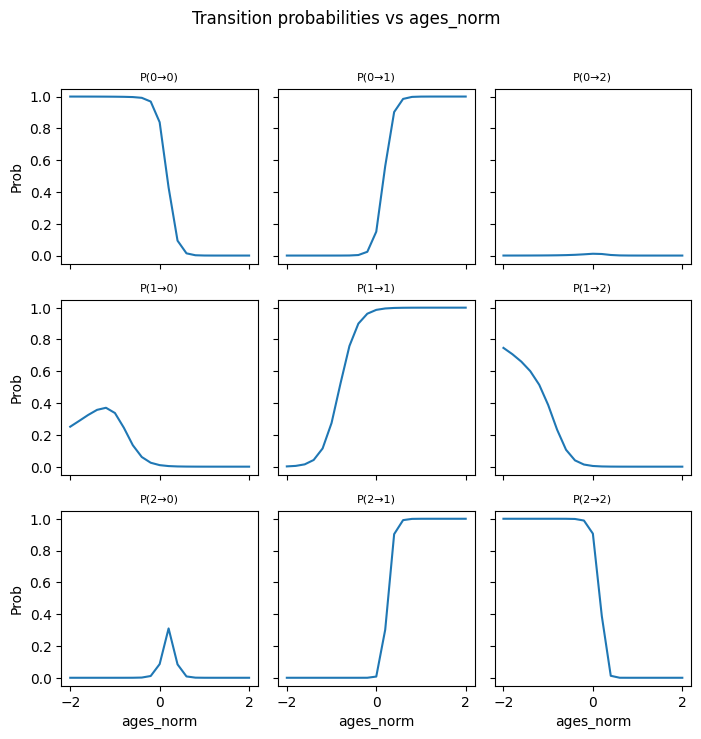
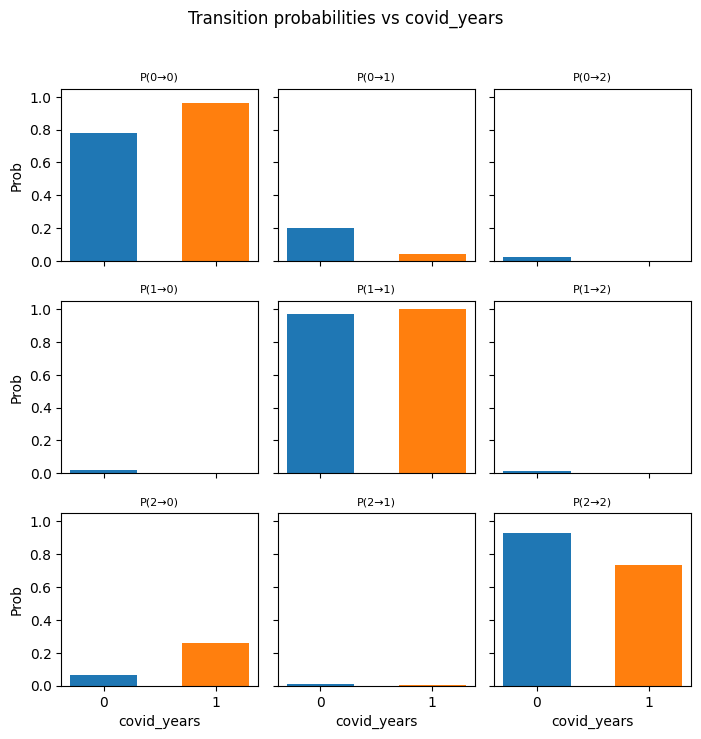
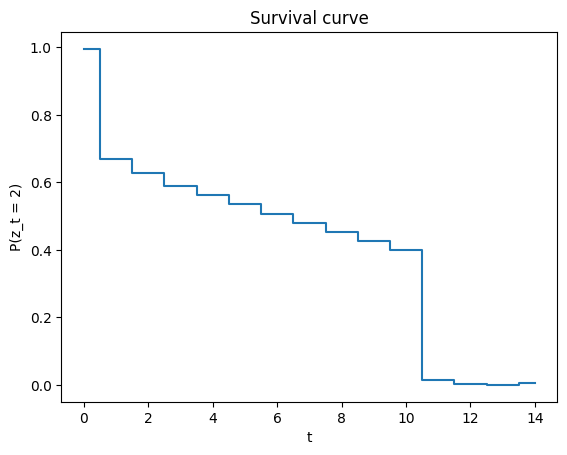
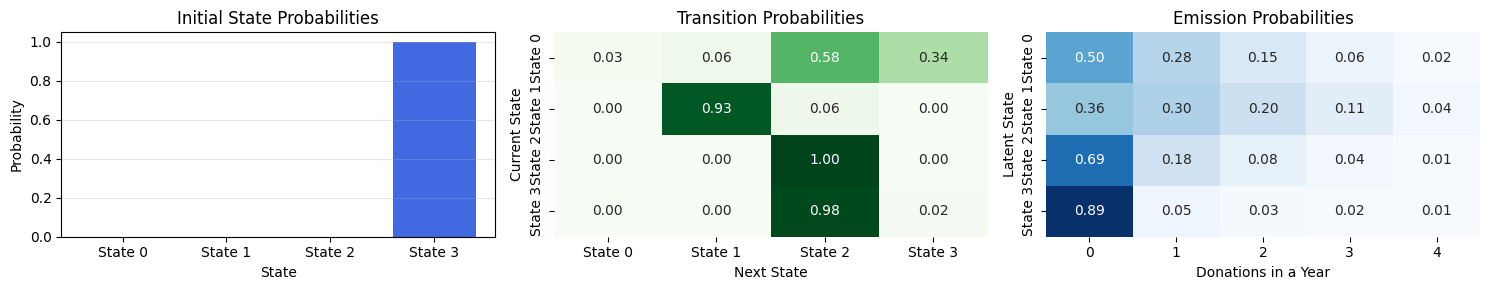
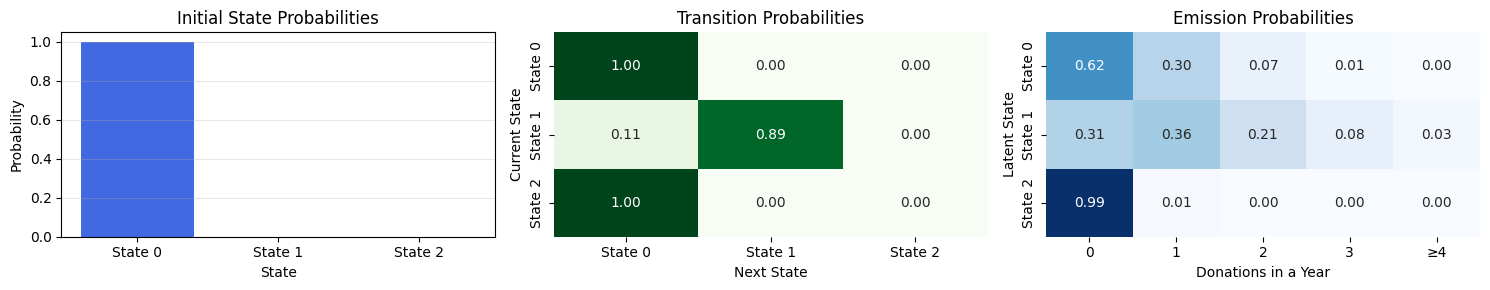
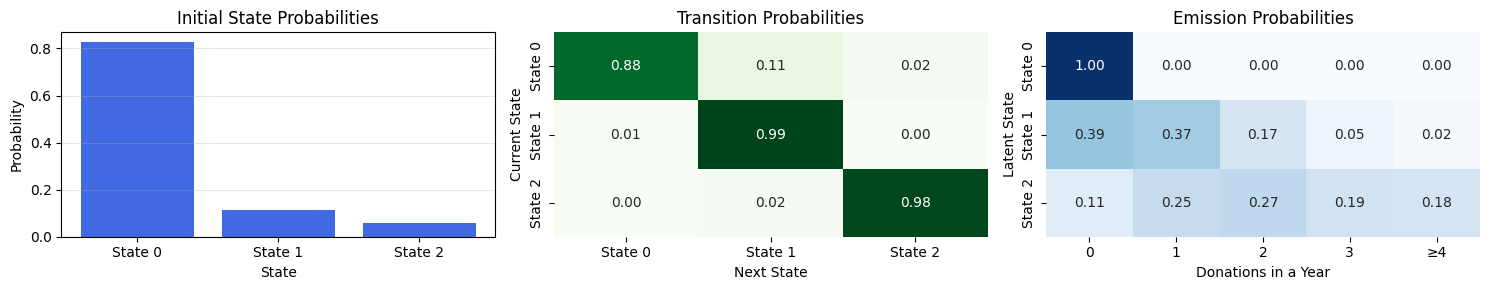
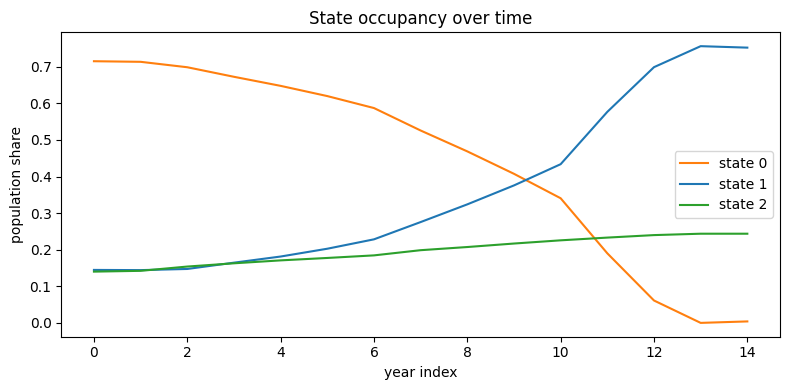
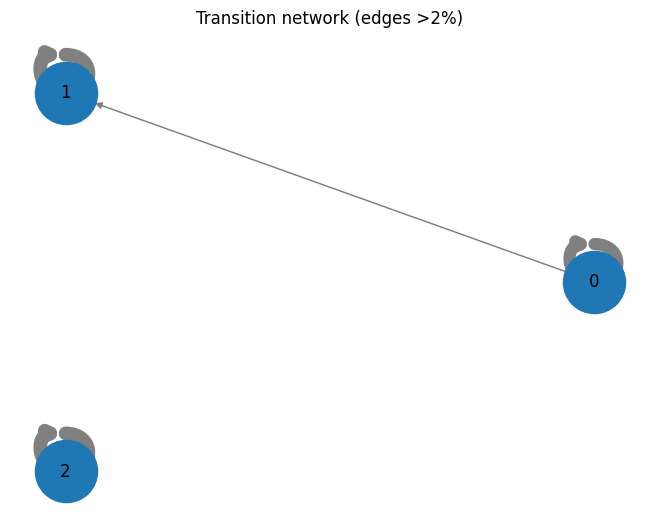
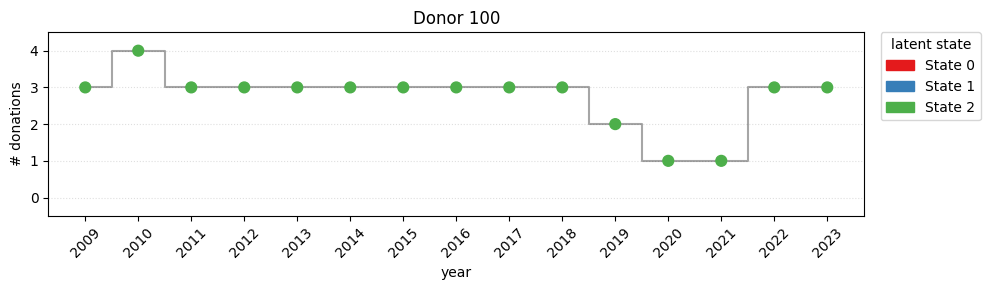
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
KeyboardInterrupt Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[253], line 91
87 svi = SVI(model, guide, Adam({"lr":0.03,"betas":(0.9,0.999),"weight_decay":1e-4}),
88 loss=TraceEnum_ELBO(max_plate_nesting=1))
90 for step in range(5_000):
---> 91 loss = svi.step(obs_torch, full_cov_torch)
92 if step % 500 == 0:
93 print(f"{step:5d} ELBO = {loss:,.0f}")
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\infer\svi.py:145, in SVI.step(self, *args, **kwargs)
143 # get loss and compute gradients
144 with poutine.trace(param_only=True) as param_capture:
--> 145 loss = self.loss_and_grads(self.model, self.guide, *args, **kwargs)
147 params = set(
148 site["value"].unconstrained() for site in param_capture.trace.nodes.values()
149 )
151 # actually perform gradient steps
152 # torch.optim objects gets instantiated for any params that haven't been seen yet
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\infer\traceenum_elbo.py:451, in TraceEnum_ELBO.loss_and_grads(self, model, guide, *args, **kwargs)
443 """
444 :returns: an estimate of the ELBO
445 :rtype: float
(...) 448 Performs backward on the ELBO of each particle.
449 """
450 elbo = 0.0
--> 451 for model_trace, guide_trace in self._get_traces(model, guide, args, kwargs):
452 elbo_particle = _compute_dice_elbo(model_trace, guide_trace)
453 if is_identically_zero(elbo_particle):
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\infer\traceenum_elbo.py:394, in TraceEnum_ELBO._get_traces(self, model, guide, args, kwargs)
392 q.put(poutine.Trace())
393 while not q.empty():
--> 394 yield self._get_trace(model, guide, args, kwargs)
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\infer\traceenum_elbo.py:339, in TraceEnum_ELBO._get_trace(self, model, guide, args, kwargs)
334 def _get_trace(self, model, guide, args, kwargs):
335 """
336 Returns a single trace from the guide, and the model that is run
337 against it.
338 """
--> 339 model_trace, guide_trace = get_importance_trace(
340 "flat", self.max_plate_nesting, model, guide, args, kwargs
341 )
343 if is_validation_enabled():
344 check_traceenum_requirements(model_trace, guide_trace)
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\infer\enum.py:60, in get_importance_trace(graph_type, max_plate_nesting, model, guide, args, kwargs, detach)
58 model_trace, guide_trace = unwrapped_guide.get_traces()
59 else:
---> 60 guide_trace = poutine.trace(guide, graph_type=graph_type).get_trace(
61 *args, **kwargs
62 )
63 if detach:
64 guide_trace.detach_()
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\trace_messenger.py:216, in TraceHandler.get_trace(self, *args, **kwargs)
208 def get_trace(self, *args, **kwargs) -> Trace:
209 """
210 :returns: data structure
211 :rtype: pyro.poutine.Trace
(...) 214 Calls this poutine and returns its trace instead of the function's return value.
215 """
--> 216 self(*args, **kwargs)
217 return self.msngr.get_trace()
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\trace_messenger.py:191, in TraceHandler.__call__(self, *args, **kwargs)
187 self.msngr.trace.add_node(
188 "_INPUT", name="_INPUT", type="args", args=args, kwargs=kwargs
189 )
190 try:
--> 191 ret = self.fn(*args, **kwargs)
192 except (ValueError, RuntimeError) as e:
193 exc_type, exc_value, traceback = sys.exc_info()
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\handlers.py:567, in queue.<locals>.wrapper.<locals>._fn(*args, **kwargs)
560 try:
561 ftr = trace(
562 escape(
563 replay(wrapped, trace=next_trace), # noqa: F821
564 escape_fn=functools.partial(escape_fn, next_trace),
565 )
566 )
--> 567 return ftr(*args, **kwargs)
568 except NonlocalExit as site_container:
569 site_container.reset_stack()
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\trace_messenger.py:191, in TraceHandler.__call__(self, *args, **kwargs)
187 self.msngr.trace.add_node(
188 "_INPUT", name="_INPUT", type="args", args=args, kwargs=kwargs
189 )
190 try:
--> 191 ret = self.fn(*args, **kwargs)
192 except (ValueError, RuntimeError) as e:
193 exc_type, exc_value, traceback = sys.exc_info()
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\messenger.py:32, in _context_wrap(context, fn, *args, **kwargs)
25 def _context_wrap(
26 context: "Messenger",
27 fn: Callable,
28 *args: Any,
29 **kwargs: Any,
30 ) -> Any:
31 with context:
---> 32 return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\messenger.py:32, in _context_wrap(context, fn, *args, **kwargs)
25 def _context_wrap(
26 context: "Messenger",
27 fn: Callable,
28 *args: Any,
29 **kwargs: Any,
30 ) -> Any:
31 with context:
---> 32 return fn(*args, **kwargs)
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\poutine\messenger.py:32, in _context_wrap(context, fn, *args, **kwargs)
25 def _context_wrap(
26 context: "Messenger",
27 fn: Callable,
28 *args: Any,
29 **kwargs: Any,
30 ) -> Any:
31 with context:
---> 32 return fn(*args, **kwargs)
Cell In[253], line 80, in guide(obs, cov)
78 for t in range(1, T):
79 logits_q = (trans_W_q[z_prev] * cov[:, t, None, :]).sum(-1) + trans_b_q[z_prev]
---> 80 z_prev = pyro.sample(f"z_{t}", dist.Categorical(logits=logits_q))
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\pyro\distributions\distribution.py:26, in DistributionMeta.__call__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
24 if result is not None:
25 return result
---> 26 return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
File c:\Users\erik4\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Lib\site-packages\torch\distributions\categorical.py:67, in Categorical.__init__(self, probs, logits, validate_args)
65 raise ValueError("`logits` parameter must be at least one-dimensional.")
66 # Normalize
---> 67 self.logits = logits - logits.logsumexp(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
68 self._param = self.probs if probs is not None else self.logits
69 self._num_events = self._param.size()[-1]
KeyboardInterrupt: